TRABID inhibition activates cGAS/STING-mediated anti-tumor

The nucleosome-tethering residue of cGAS is necessary for micronuclei

Ubiquitin ligase enzymes and de-ubiquitinating enzymes regulate innate immunity in the TLR, NLR, RLR, and cGAS-STING pathways

Polyubiquitin linkage profiles in three models of proteolytic stress suggest the etiology of Alzheimer disease. - Abstract - Europe PMC

TET2-mediated tumor cGAS triggers endothelial STING activation to regulate vasculature remodeling and anti-tumor immunity in liver cancer

The cGAS–STING pathway and cancer

Recombinant Human His6-ZRANB1/Trabid Protein, CF E-560-050: R&D Systems

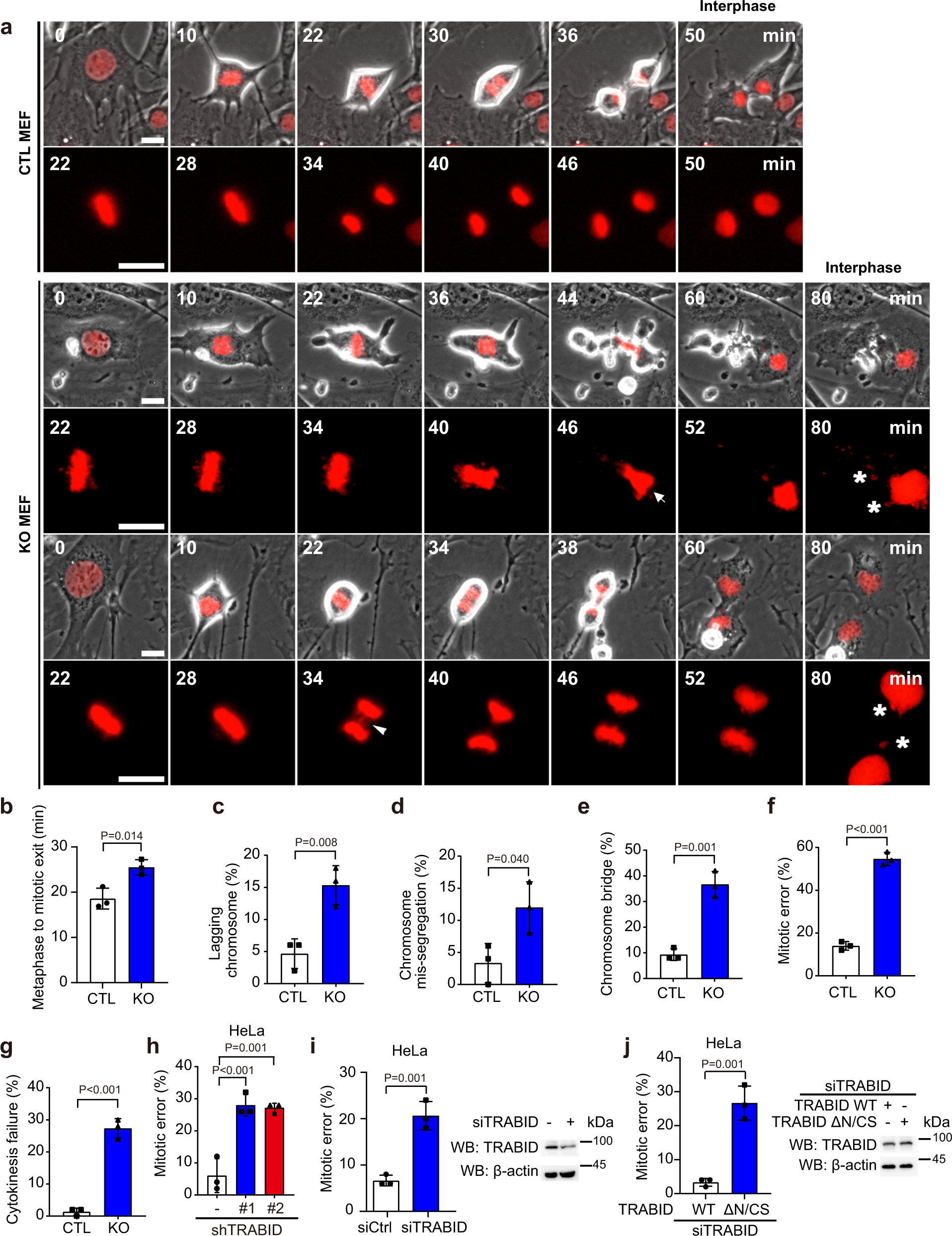
TRABID inhibition activates cGAS/STING-mediated anti-tumor immunity through mitosis and autophagy dysregulation

CGAS promoted the clearance of micronuclei through autophagy. (A)
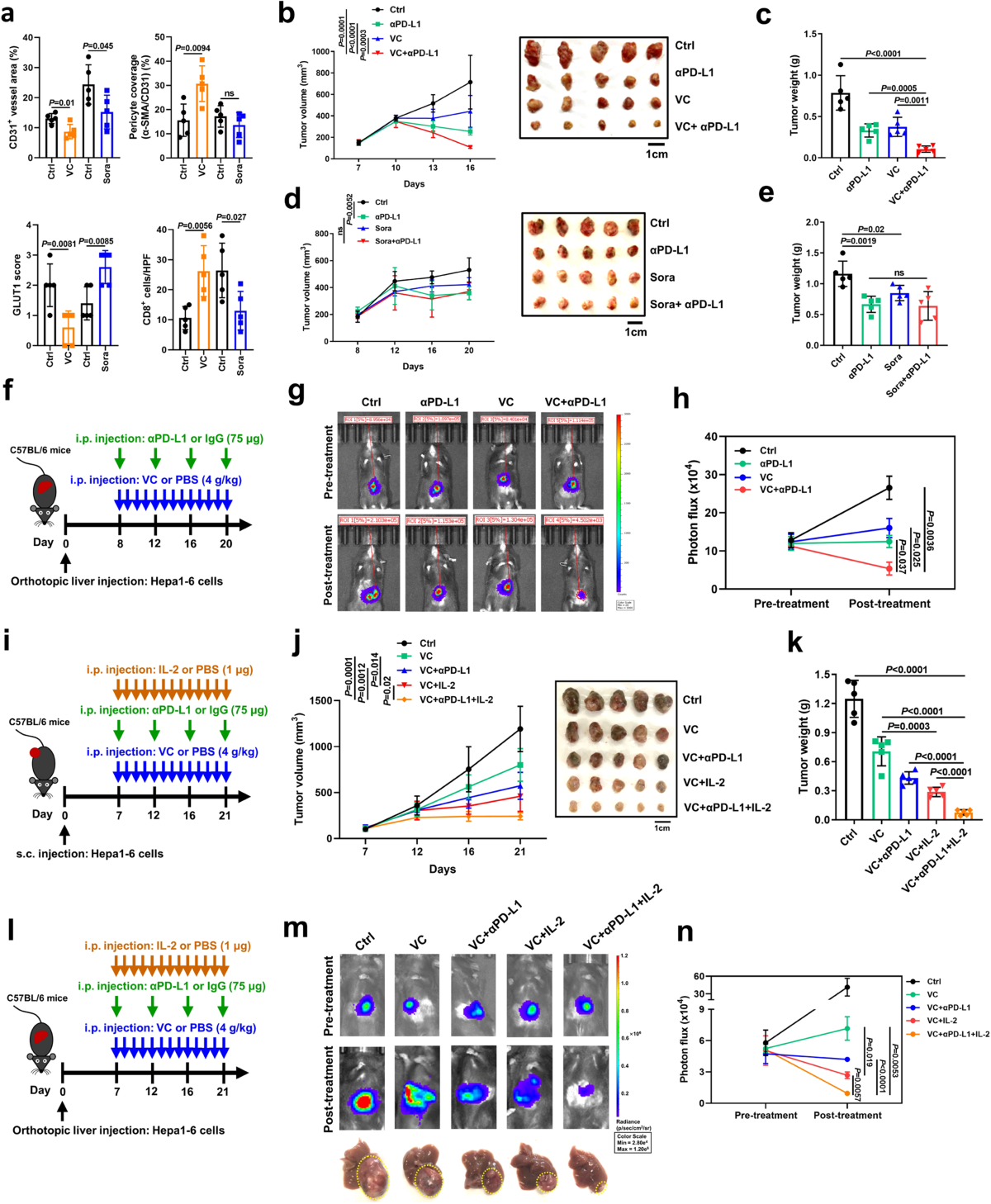
TET2-mediated tumor cGAS triggers endothelial STING activation to regulate vasculature remodeling and anti-tumor immunity in liver cancer

TRABID inhibition activates cGAS/STING-mediated anti-tumor immunity through mitosis and autophagy dysregulation
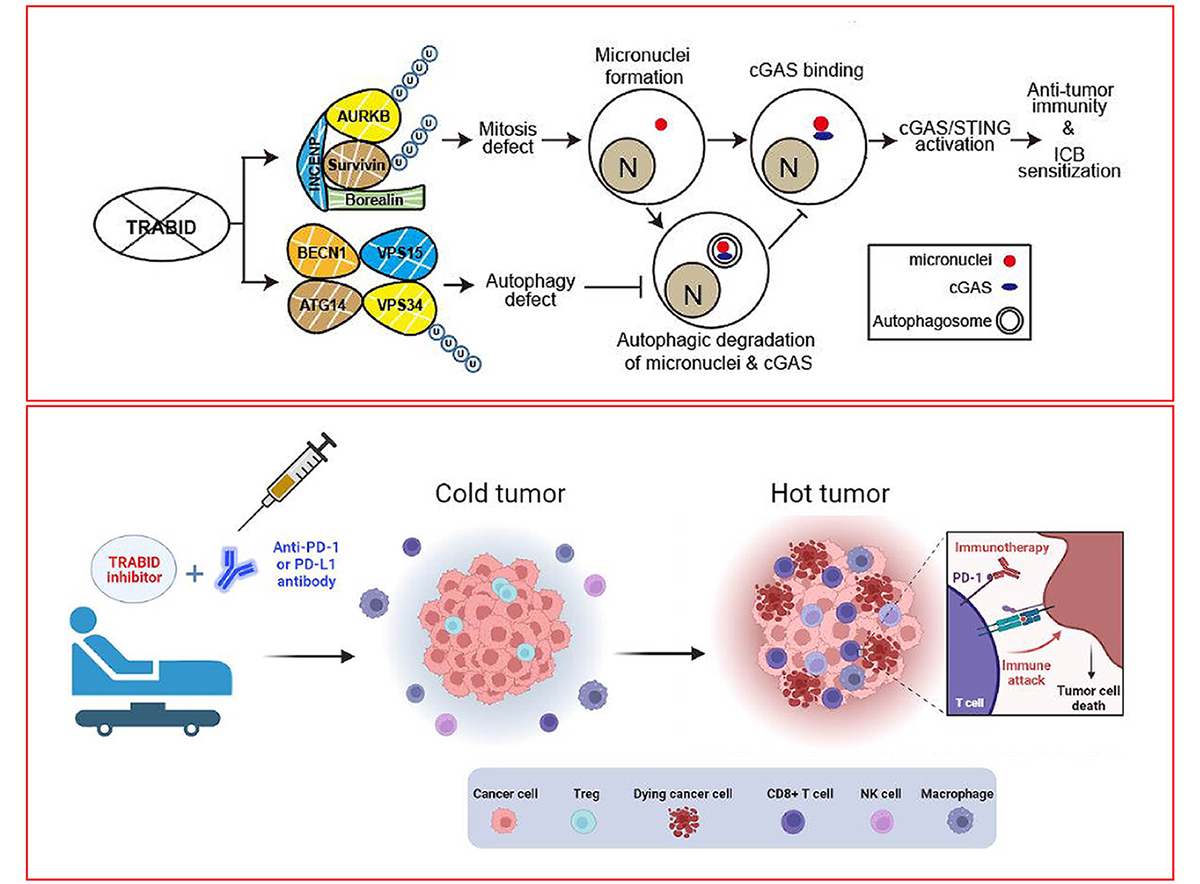
IBC - 精彩研究成果: 提升癌症免疫治療功效的新靶標

ZRANB1 Is an EZH2 Deubiquitinase and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Breast Cancer. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Anti-tumor mechanism of cGAS-STING pathway.Fragments of DNA from cancer









